Hive使用场景
数据仓库( Data Warehouse ),是为企业所有决策制定过程,提供所有系统数据支持的战略集合。通过对数据仓库中数据的分析,可以帮助企业,改进业务流程、控制成本、提高产品质量等。 数据仓库,并不是数据的最终目的地,而是为数据最终的目的地做好准备。这些准备包括对数据的:清洗,转义,分类,重组,合并,拆分,统计等等。
数仓分层:
- ODS:original data store 原始数据层,存放原始数据,直接加载原始日志、数据,数据保持原貌不做处理。
- DIM:dimensions 公共维度汇总层,保存维度数据,主要是对业务事实的描述信息,列如何人、何时、何地。
- DWD:data warehouse detail 明细数据层:对ODS层数据进行清洗(去除空值,脏数据,超过极限范围的数据)、脱敏等。保存业务事实明细,一行信息代表一次业务行动,例如一次下单。
- DWS:data warehouse service 以DWD为基础,按天进行轻度汇总。一行信息代表一个主题对象一天的汇总行为,例如一个用户一天下单次数。
- DWT:data warehouse topic 以DWS为基础,对数据进行累积汇总。一行信息代表一个主题对象的累积行为,例如一个用户从注册那天开始至今一共下了多少次单
- ADS:application data store ADS层,为各种统计报表提供数据
数据仓库为什么要分层:
- 把复杂问题简单化 将复杂的任务分解成多层来完成,每一层只处理简单的任务,方便定位问题。
- 减少重复开发 规范数据分层,通过的中间层数据,能够减少极大的重复计算,增加一次计算结果的复用性。
- 隔离原始数据 不论是数据的异常还是数据的敏感性,使真实数据与统计数据解耦开。
Hive的安装以及配置
环境变量
#[/etc/profile.d/env.sh]
export HIVE_HOME=/opt/module/hive
pathmunge $HIVE_HOME/bin
配置文件
<!-- [/$HIVE_HOME/conf/hive-site.xml] -->
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<?xml-stylesheet type="text/xsl" href="configuration.xsl"?>
<configuration>
<property>
<name>javax.jdo.option.ConnectionURL</name>
<value>jdbc:mysql://hadoop101:3306/hive_metastore?useSSL=false&
useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF-8</value>
</property>
<property>
<name>javax.jdo.option.ConnectionDriverName</name>
<value>com.mysql.jdbc.Driver</value>
</property>
<property>
<name>javax.jdo.option.ConnectionUserName</name>
<value>root</value>
</property>
<property>
<name>javax.jdo.option.ConnectionPassword</name>
<value>000000</value>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.metastore.warehouse.dir</name>
<value>/user/hive/warehouse</value>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.server2.thrift.port</name>
<value>10000</value>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.server2.thrift.bind.host</name>
<value>hadoop101</value>
</property>
<!-- Hive元数据存储的验证 -->
<property>
<name>hive.metastore.schema.verification</name>
<value>false</value>
</property>
<!-- 元数据存储授权 -->
<property>
<name>hive.metastore.event.db.notification.api.auth</name>
<value>false</value>
</property>
<!--Spark依赖位置(注意:端口号8020必须和namenode的端口号一致)-->
<property>
<name>spark.yarn.jars</name>
<value>hdfs://hadoop101:8020/spark-jars/*</value>
</property>
<!--Hive执行引擎-->
<property>
<name>hive.execution.engine</name>
<value>spark</value>
</property>
<!--Hive和Spark连接超时时间-->
<property>
<name>hive.spark.client.connect.timeout</name>
<value>10000ms</value>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.cli.print.header</name>
<value>true</value>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.cli.print.current.db</name>
<value>true</value>
</property>
</configuration>
hive支持中文
在Hive元数据存储的Mysql数据库中,执行以下SQL:
-- 在mysql中的hive元数据库中执行
alter table hive_metastore.COLUMNS_V2 modify column COMMENT varchar(256) character set utf8mb4 COLLATE utf8mb4_unicode_ci;
alter table hive_metastore.DBS modify column DBS.DESC varchar(256) character set utf8mb4 COLLATE utf8mb4_unicode_ci;
alter table hive_metastore.TABLE_PARAMS modify column PARAM_VALUE varchar(4000) character set utf8mb4 COLLATE utf8mb4_unicode_ci;
alter table hive_metastore.PARTITION_PARAMS modify column PARAM_VALUE varchar(4000) character set utf8mb4 COLLATE utf8mb4_unicode_ci;
alter table hive_metastore.PARTITION_KEYS modify column PKEY_COMMENT varchar(4000) character set utf8mb4 COLLATE utf8mb4_unicode_ci;
alter table hive_metastore.PARTITION_KEY_VALS modify column PART_KEY_VAL varchar(256) character set utf8mb4 COLLATE utf8mb4_unicode_ci;
alter table hive_metastore.INDEX_PARAMS modify column PARAM_VALUE varchar(4000) character set utf8mb4 COLLATE utf8mb4_unicode_ci;
修改hive-site.xml中Hive读取元数据的编码
<property>
<name>javax.jdo.option.ConnectionURL</name>
<value>jdbc:mysql://hadoop101:3306/metastore?useSSL=false&
useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF-8</value>
</property>
注意:在修改之前创建的表不起作用
HQL
Create-Table-As-Select (CTAS).
CREATE TABLE tmp_emp2 as SELECT * FROM tmp_emp1;
CREATE TABLE tmp_emp3 like tmp_emp1;
当需要写一个比较复杂的HQL查询语句时,推荐使用CTE(Common Table Expression)重写嵌套的查询语句,如下:
-- 查询多个临时表 对数据集合汇总 并插入到表格中
with(select clause) as tmp1,
... as tmp2,
....
insert overwrite table table name partition(dt)
select ... from ... join ... on ...
hive中的表分为managed(托管表也叫做内部表)、external(外部表)、temporary(临时表)。临时表只对当前的用户session可见,并且在session结束后自动删除。不支持分区以及创建索引。 hive表默认都是内部表,hive控制其数据的生命周期。删除内部表时元数据和数据都会被删除。对于外部表,hive控制元数据,删除外部表时只会删除表的定义,保留表的数据。 -- 删除表:drop table(truncate table不允许对外部表操作)
-- 清空外部表
alter table ads_user_retention set TBLPROPERTIES('EXTERNAL'='false');
truncate table ads_user_retention;
alter table ads_user_retention set TBLPROPERTIES('EXTERNAL'='true');
-- 修复外部表数据
msck repair table tablename
复杂数据类型定义
1)map结构数据定义
map<string,string>
2)array结构数据定义
array<string>
3)struct结构数据定义
struct<id:int,name:string,age:int>
4)struct和array嵌套定义
array<struct<id:int,name:string,age:int>>
Hive中的join
Hive是基于Hadoop的一个数据仓库工具,可以将结构化的数据文件映射为一张数据库表,并提供简单的sql查询功能,可以将sql语句转换为MapReduce任务进行运行。 sql中的连接查询有inner join(内连接)、left join(左连接)、right join(右连接)、full join(全连接)left semi join(左半连接) 五种方式,它们之间其实并没有太大区别,仅仅是查询出来的结果有所不同。
union 和 full join on 的区别,“full join on 列合并和 union 行合并”:
full join 使用on条件时,select * 相当于把两个表(左表有m列p行和右表有n列q行)的所有列拼接成了一个有m+n列的结果表。
select * from table1 full join table2 on(table1.student_no=table2.student_no);
而union相当于把相当于把两个查询结果(左查询结果表有m列p行和右查询结果表有n列q行)的所有行进行了拼接,形成具有p+q行的查询结果。
select student_no tb1_student_no,student_name from table1 union select student_no as tb2_student_no,class_no from table2;
注意此时 ,左查询结果表和右查询结果表,必须有相同的列,即m=q相等,否则会报如下错误:
hive> select student_no tb1_student_no,student_name from table1 union select class_no from table2;
FAILED: SemanticException Schema of both sides of union should match.
union 和 union all 的区别
使用场合:
如果我们需要将两个select语句的结果作为一个整体显示出来,我们就需要用到union或者union all关键字。union的作用是将多个结果合并在一起显示出来。
注意事项:
union 和 union all都可以将多个结果集合并,而不仅仅是两个,你可以将多个结果集串起来。
使用union和union all必须保证各个select 集合的结果有相同个数的列,并且每个列的类型是一样的。但列名则不一定需要相同,oracle会将第一个结果的列名作为结果集的列名。
注意hive中int不能隐式转换成bigint 先转string 再转 bigint
二者区别:
Union:对两个结果集进行并集操作,不包括重复行,同时进行默认规则的排序。Union在进行表链接后会筛选掉重复的记录,所以在表连接后会对所产生的结果集进行排序运算,删除重复的记录再返回结果。
实际大部分应用中是不会产生重复的记录,最常见的是过程表与历史表Union。
Union All:对两个结果集进行并集操作,包括重复行,不进行排序。如果返回的两个结果集中有重复的数据,那么返回的结果集就会包含重复的数据了。
Inner join是最简单的关联操作
如果有on 条件的话,则两边关联只取交集。
select * from table1 join table2 on table1.student_no=table2.student_no ;
笛卡尔积:如果没有on条件的话,则是左表和右表的列通过笛卡尔积的形式表达出来,下面两个sql就是求笛卡尔积:
select * from table1 join table2;
select * from table1 inner join table2;
比如table1有m行,table2有n行,最终的结果将有 m*n行
Inner join不使用 join 关键字的隐式连接,注意只适用于inner join:
SELECT
emp.name, emph.sin_number
FROM
employee emp, employee_hr emph -- Only applies for inner join
WHERE
emp.name = emph.name;
outer join分为left outer join、right outer join和full outer join:
left outer join是以左表驱动,右表不存在的key均赋值为null;right outer join是以右表驱动,左表不存在的key均赋值为null;
full outer join全表关联,即是左外连接和右外连接结果集合求并集 ,左右表均可赋值为null。(而不是将两表完整的进行笛卡尔积操作,这种表述是错误的)
如果full join不加on过滤条件,计算结果也是笛卡尔积:
select * from table1 a full join table2 b ;
left semi join 和 inner join
LEFT SEMI JOIN:
semi join (即等价于left semi join)最主要的使用场景就是解决exist in。LEFT SEMI JOIN(左半连接)是 IN/EXISTS 子查询的一种更高效的实现。
Hive 没有实现 IN/EXISTS 子查询前,你可以用 LEFT SEMI JOIN 重写你的子查询语句。LEFT SEMI JOIN 的限制是, JOIN 子句中右边的表只能在
ON 子句中设置过滤条件,在 WHERE 子句、SELECT 子句或其他地方过滤都不行。
SELECT a.key, a.value
FROM a
WHERE a.key in
(SELECT b.key
FROM B);
可以被重写为:
SELECT a.key, a.val
FROM a LEFT SEMI JOIN b on (a.key = b.key)
注意,在hive 2.1.1版本中,支持子查询,使用in 和 not in关键字,以下两个SQL都是正确的:
SELECT * FROM TABLE1 WHERE table1.student_no NOT IN (SELECT table2.student_no FROM TABLE2);
SELECT * FROM TABLE1 WHERE table1.student_no IN (SELECT table2.student_no FROM TABLE2);
inner join:
INNER JOIN等价于 JOIN,你可以理解为 JOIN是 INNER JOIN 的缩写。
区别:
HIVE中都是等值连接(hive 2.2.0版本中支持非等值连接),在JOIN使用的时候,两种写法在理论上是可以达到相同的效果的,但是由于实际情况的不一样,子表中数据的差异导致结果也不太一样。
当子表中存在重复的数据,使用JOIN ON的时候,A,B表会关联出两条记录,因为ON上的条件符合;
而使用LEFT SEMI JOIN时,当A表中的记录,在B表上产生符合条件之后就返回,不会再继续查找B表记录了,所以如果B表有重复,也不会产生重复的多条记录。
Hive常用函数
str_to_map(text,delimiter1,delimiter2) 将键值对字符串转换成map对象
text: k/v字符串 delimiter1: kv对 切割符 delimiter2: 键值k/v 切割符
name_struct(name1,val1,name2,val2...)
creates a struct with the given names and values
列转行:concat_ws(saparator,collect_set())
行转列:later view(explode(..set))
collect_set(...elements)
返回一系列去重的对象集合 collect_list()不去重
concat_ws([str| array(str)]) 将给定的字符串连接起来
nvl(value,default value)
return default value if value is null else return value
coalesce(value1,value2...)
return the first not-null value
posexplode(a)
- behaves like explode for arrays, but includes
the position (starting with 0) of items in the original array
日期处理函数:
1)date_format函数(根据格式整理日期)
hive (gmall)> select date_format('2020-06-14','yyyy-MM');
2020-06
2)date_add/date_sub函数(加减日期)
hive (gmall)> select date_add('2020-06-14',-1);
2020-06-13
hive (gmall)> select date_add('2020-06-14',1);
2020-06-15
3)next_day函数
取当前天的下一个周一
hive (gmall)> select next_day('2020-06-14','MO');
2020-06-15
取当前周的周一
hive (gmall)> select date_add(next_day('2020-06-14','MO'),-7);
2020-06-8
4)last_day函数(求当月最后一天日期)
hive (gmall)> select last_day('2020-06-14');
2020-06-30
时间处理:
1)from_unixtime(unix_time, format)
- returns unix_time in the specified format
2)unix_timestamp(date[, pattern])
- Converts the time to a number
pivot on spark-sql/oracle
– pivot ,Spark-sql 、Oracle特有关键词,即旋转,将指列的字段值,旋转成为多个列。并且可以指定某些列成为旋转列的聚合值。
假设有表test_order_info如下,现在需求求出每个user购买各个product的amount。
| uname | product | age | city | amount |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| zhang3 | tv | 22 | bj | 3000 |
| li4 | notebook | 41 | bj | 8000 |
| wang5 | phone | 32 | sh | 4000 |
| zhao6 | notebook | 22 | sz | 3000 |
| zhang3 | phone | 22 | bj | 3000 |
| li4 | tv | 41 | sz | 4000 |
select * from
(select uname,product,age,amount from test_order_info)oi
pivot ( sum(amount) as amt for product in ('tv','notebook','phone' ));
-- result 注意旋转列tv/notebook/phone列名省略了_amt
uname age tv notebook phone
zhang3 22 3000 null 3000
zhao6 22 null 3000 null
li4 41 4000 8000 null
wang5 32 null null 4000
原理说明
把整个表整理成3种列:维度列、旋转列、聚合列
-- 格式:
select * from table_name
pivot ( sum(聚合列) as 列标识 for 旋转列 in( 旋转列值1 ,旋转列值2,旋转列值3) )
除了旋转列和聚合列,默认都是维度列,如果存在这三种以外的字段,需要提前用子查询去除。
窗口函数:
- row_number(): Assigns a unique sequence number starting from 1 to each row, according to the partition and order specification.
- rank(): Ranks items in a group, such as finding the top N rows for specific conditions.
- dense_rank(): Similar to rank, but leaves no gaps in the ranking sequence when there are ties. For example, if we rank a match using dense_rank and have two players tied for second place, we would see that the two players were both in second place and that the next person is ranked third. However, the rank function would rank two people in second place, but the next person would be in fourth place.
- percent_rank(): Uses rank values rather than row counts in its numerator as (current rank - 1)/(total number of rows - 1). Therefore, it returns the percentage rank of a value relative to a group of values.
- LEAD(value_expr[,offset[,default]]) return data from the next row
The number of rows to lead can optionally be specified. If the number of rows to lead is not specified, the lead is one row. Returns default/null when the lead for the current row extends beyond the end of the window. - LAG(value_expr[,offset[,default]]) return data from a previous row
The number of rows to lag can optionally be specified. If the number of rows to lag is not specified, the lag is one row. Returns default/null when the lag for the current row extends before the beginning of the window. - FIRST_VALUE
This takes at most two parameters. The first parameter is the column for which you want the first value, the second (optional) parameter must be a boolean which is false by default. If set to true it skips null values. - LAST_VALUE
This takes at most two parameters. The first parameter is the column for which you want the last value, the second (optional) parameter must be a boolean which is false by default. If set to true it skips null values.
Hive表设计
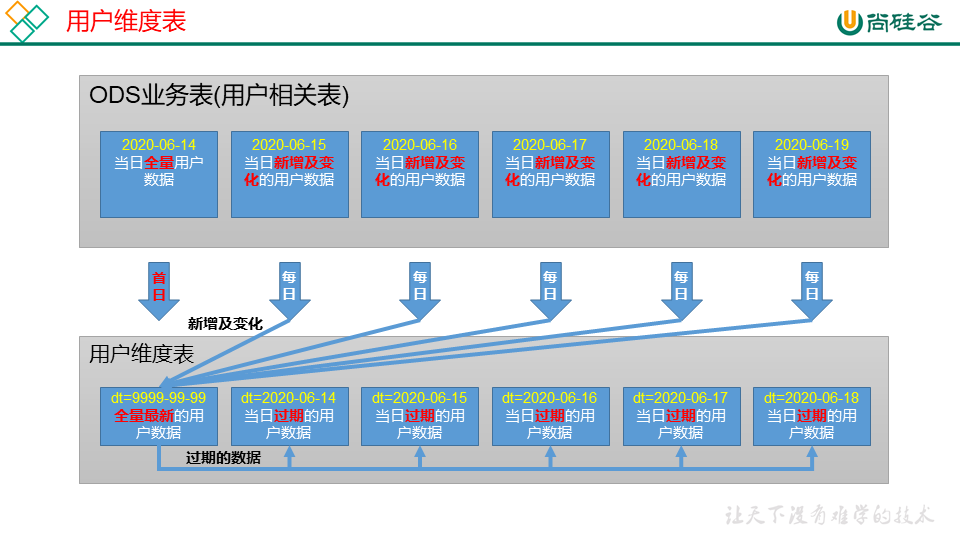
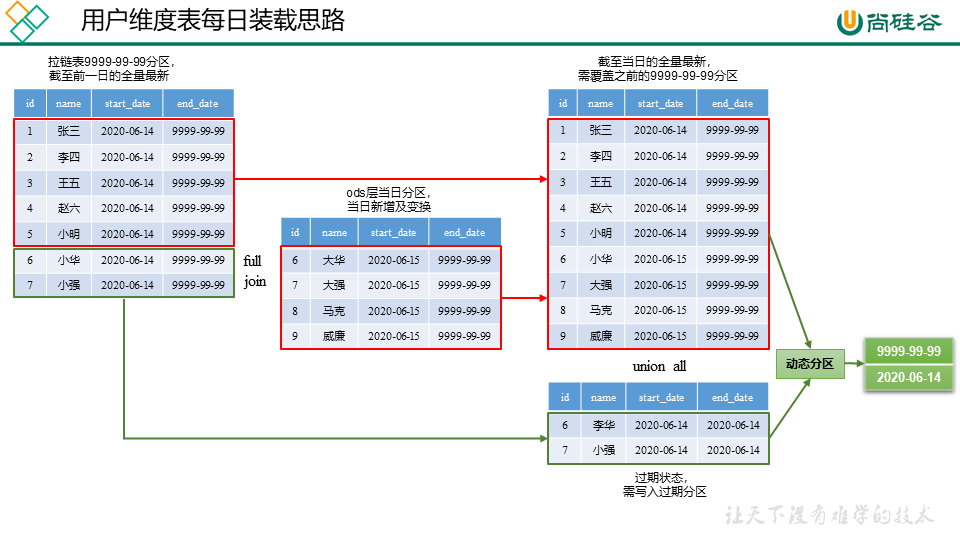
拉链表
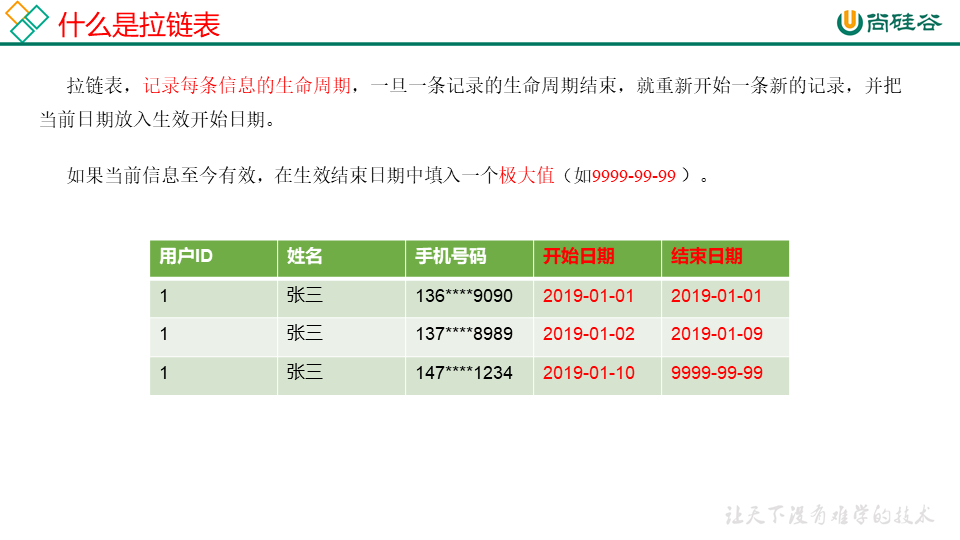
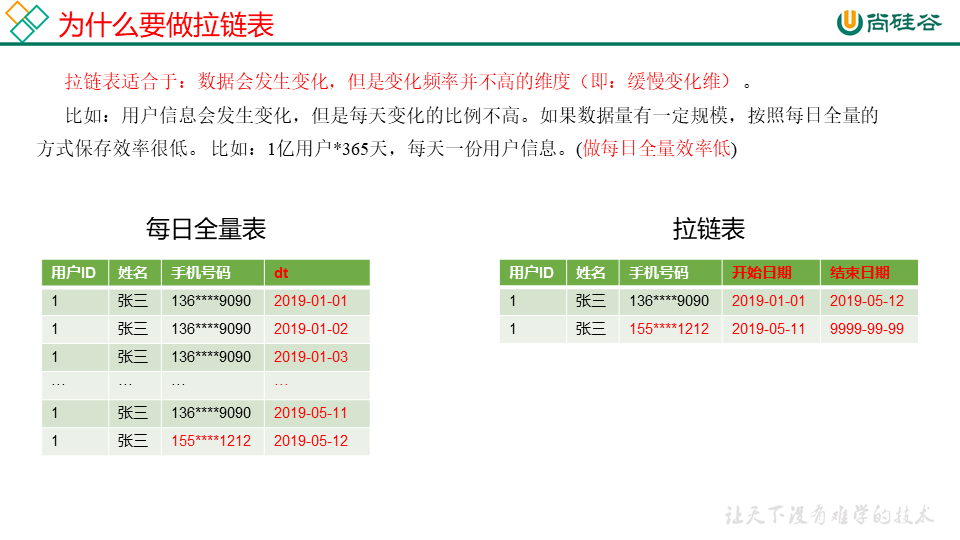
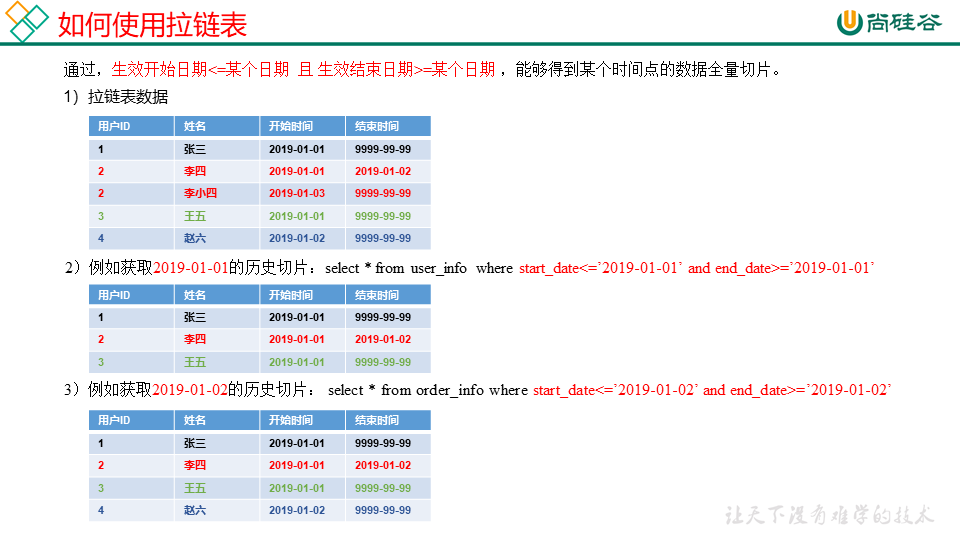
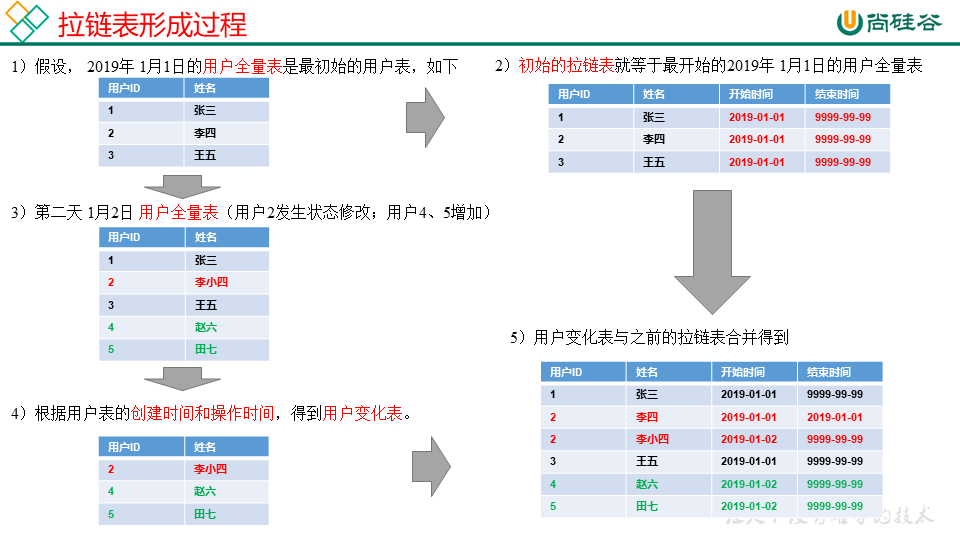

案列分析:
-- 1.建表语句
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS dim_user_info;
CREATE EXTERNAL TABLE dim_user_info(
`id` STRING COMMENT '用户id',
`name` STRING COMMENT '用户姓名',
`start_date` STRING COMMENT '开始日期',
`end_date` STRING COMMENT '结束日期'
) COMMENT '用户表'
PARTITIONED BY (`dt` STRING)
STORED AS ORC
LOCATION '/warehouse/gmall/dim/dim_user_info/'
TBLPROPERTIES ("orc.compress"="snappy");
-- 2.首日装载数据
insert overwrite table dim_user_info partition(dt='9999-99-99')
select
id,
md5(name),
'2020-06-14',
'9999-99-99'
from ods_user_info --ods层用户表
where dt='2020-06-14';
-- 3.每日装载数据
with
tmp as
(
select
old.id old_id,
old.name old_name,
old.start_date old_start_date,
old.end_date old_end_date,
new.id new_id,
new.name new_name,
new.start_date new_start_date,
new.end_date new_end_date
from
(
select
id,
md5(name) name,
start_date,
end_date
from dim_user_info
where dt='9999-99-99'
)old
full outer join
(
select
id,
md5(name) name,
'2020-06-15' start_date,
'9999-99-99' end_date
from ods_user_info
where dt='2020-06-15'
)new
on old.id=new.id
)
insert overwrite table dim_user_info partition(dt)
select
nvl(new_id,old_id),
nvl(new_name,old_name),
nvl(new_start_date,old_start_date),
nvl(new_end_date,old_end_date),
nvl(new_end_date,old_end_date) dt
from tmp
union all
select
old_id,
old_name,
old_start_date,
cast(date_add('2020-06-15',-1) as string),
cast(date_add('2020-06-15',-1) as string) dt
from tmp
where new_id is not null and old_id is not null;
-- 4.sql解析
1)tmp表全连接full (outer) join 横向聚合(列)数据
tmp表是通过昨天的最新用户维度表(dim层的 9999-99-99分区)old和
今天的用户表的新增及变化表(ods层的 2020-06-15分区)new full join后产生的,
那么数据集包含了 用户记录信息的全部更改过程。
对于full join 不匹配的 左表不存在的为null 右表不存在的也为null。
也就意味着包含了今天更改的用户(match)
今天未更改的用户(mismatch right null)
以及今天新增的用户(mismatch left null)。
用户有三种情况:
1.未更改
old_user_id new_user_id old_name new_name old_start new_start old_end new_end
1 null david null 20200614 null 99999999 null
2.更改
old_user_id new_user_id old_name new_name old_start new_start old_end new_end
2 2 sally sally1 20200614 20200615 99999999 99999999
3.新增
old_user_id new_user_id old_name new_name old_start new_start old_end new_end
null 3 null kula null 20200615 null 99999999
而我们拉链表要达到的效果是既有当天最新的用户表 还有保存更改之前的用户表 并且要分区 end_time是分区字段
nvl(value,default_value)函数 如果value为null就取default_value 否者就取value
2)select nvl(new_value,old_value) from tmp 语句
nvl(new_value,old_value) 这是取出最新的用户表信息
用户有三种情况:参照上表
1.未更改
user_id name start end
1 david 20200614 99999999
2.更改
user_id name start end
2 sally1 20200615 99999999
3.新增
user_id name start end
3 kula 20200615 99999999
这是取出20200615的最新用户信息,同时注意这些信息分区为99999999
3)根据需求我们还需要保存20200614-20200615的用户信息更改过程 怎么取呢?
select old_id, old_name, old_start, cast(date_add('2020-06-15',-1) as string) old_end,
cast(date_add('2020-06-15',-1) as string) dt from tmp
同样取出来的用户有三种情况:
1.未更改
old_user_id old_name old_start old_end
1 david 20200614 20200614
2.更改
old_user_id old_ name old_start old_end
2 sally 20200614 20200614
3.新增
old_user_id old_name old_start old_end
3 kula 20200614 20200614
我们要取的信息是:
20200615发生更改的用户 更改之前的状态 既是
old_user_id old_ name old_start old_end
2 sally 20200614 20200614
查看第一张表,我们发现只有发生更改的用户old_user_id 和 new_user_id都不为null。
通过where new_id is not null and old_id is not null子句过滤。
4)将2和3中的结果集纵向聚合(行)使用union all 比 union性能更好,就得到了我们想要的数据
1.未更改
user_id name start end
1 david 20200614 99999999
2.更改
user_id name start end
2 sally1 20200615 99999999
3.新增
user_id name start end
3 kula 20200615 99999999
4.更改之前
user_id name start end
2 sally 20200614 20200614
用户维度表
20200614分区:20200614过期的用户信息
99999999分区:最新的用户信息
Hive优化
join时的优化
map-side join: If all but one of the tables being joined are small, the join can be performed as a map only job. The query
SELECT /*+ MAPJOIN(b) */ a.key, a.value
FROM a JOIN b ON a.key = b.key
does not need a reducer. For every mapper of A, B is read completely.
The restriction is that:
- Full outer join is not supported since both the tables need to be streamed to perform a full outer join.
- A left join can only be converted into a map join if the right table is small enough to fit into memory.
- A right join can only be converted into a map join if the left table is small enough to fit into memory.
Parameters required to enable Map join:
Below are the parameters which need to be enabled in order to facilitate map side join in hive.
hive.auto.convert.join
We need to set this option true to convert the join into a map join automatically if the table size is smaller than the defined size of the parameter hive.mapjoin.smalltable.filesize (25MB).
hive.auto.convert.join.noconditionaltask
In case of three or more tables, hive generates three or more map side joins. To combine all these map joins in a single task, we need to set this option as true. If the combined size of n-1 tables is less than the defined size of the parameter hive.auto.convert.join.noconditionaltask.size (10MB), it will convert the join into a map join automatically.
reduce-side join(common join):
Hive converts joins over multiple tables into a single map/reduce job if for every table the same column is used in the join clauses.In every map/reduce stage of the join, the last table in the sequence is streamed through the reducers where as the others are buffered. Therefore, it helps to reduce the memory needed in the reducer for buffering the rows for a particular value of the join key by organizing the tables such that the largest tables appear last in the sequence.
In every map/reduce stage of the join, the table to be streamed can be specified via a hint.
SELECT /*+ STREAMTABLE(a) */ a.val, b.val, c.val
FROM a JOIN b ON (a.key = b.key1) JOIN c ON (c.key = b.key1)
all the three tables are joined in a single map/reduce job and the values for a particular value of the key for tables b and c are buffered in the memory in the reducers. Then for each row retrieved from a, the join is computed with the buffered rows. If the STREAMTABLE hint is omitted, Hive streams the rightmost table in the join.
Joins occur BEFORE WHERE CLAUSES: So, if you want to restrict the OUTPUT of a join, a requirement should be in the WHERE clause, otherwise it should be in the JOIN clause. A big point of confusion for this issue is partitioned tables:
SELECT a.val, b.val FROM a LEFT OUTER JOIN b ON (a.key=b.key)
WHERE a.ds='2009-07-07' AND b.ds='2009-07-07'
will join a on b, producing a list of a.val and b.val. The WHERE clause, however, can also reference other columns of a and b that are in the output of the join, and then filter them out. However, whenever a row from the JOIN has found a key for a and no key for b, all of the columns of b will be NULL, including the ds column. This is to say, you will filter out all rows of join output for which there was no valid b.key, and thus you have outsmarted your LEFT OUTER requirement. In other words, the LEFT OUTER part of the join is irrelevant if you reference any column of b in the WHERE clause. Instead, when OUTER JOINing, use this syntax:
SELECT a.val, b.val FROM a LEFT OUTER JOIN b
ON (a.key=b.key AND b.ds='2009-07-07' AND a.ds='2009-07-07')
..the result is that the output of the join is pre-filtered, and you won’t get post-filtering trouble for rows that have a valid a.key but no matching b.key. The same logic applies to RIGHT and FULL joins.
Hive的全外连接(full outter join一定不能进行mapjoin)在MR的层面上是怎么进行的呢?
全外连接要保留所有的key,那么两个表必然要进入map/reduce stage,同时在reduce端要保证同一个key(join 字段)进入到同一个reduce当中,并且数据应该是key组内有序的,也就是说reduce端的数据应该先按key分区再按表分组。 我们可以通过组合键来实现,至少要两个字段key(join 键)还有flag(表的标记,假设左表为0,右表为1)。首先需要分区器partitioner根据key分区,还需要分组比较器comparator。根据key,flag(假设是升序)进行排序。 两个表都做为map端的输入并进行判断根据表设置flag,将(combkey,value)写出去。经过shuffle 和 sort 之后在reduce端开始聚合。对于每一个key左表的数据一定先到,如果右表匹配那接着就是右表的数据。如果没有匹配的那么接下就是左表的下一个key的记录(左右两表key值不重复的情况下,一般情况下不会重复)。即使重复也可以通过判断进行处理, 因为不管多少重复的数据对于同一个key左表的数据一定比右表先到。 这样只要将reduce端的数据遍历完我们就能得到join后的结果。
Hive坑点
- lzo的index文件对hive表数据有影响 会多出一行&空行
解决办法:使用snappy压缩